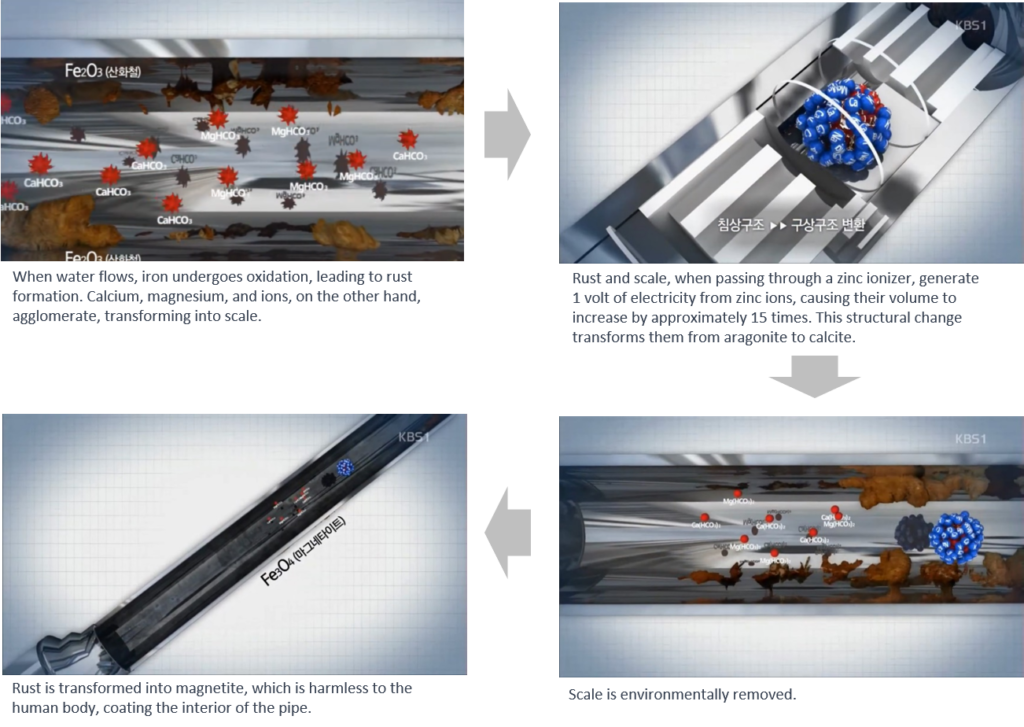
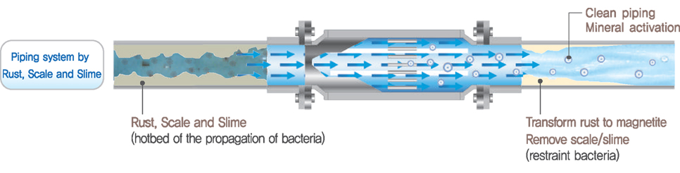
Zinc ionization for water treatment is generally considered to be environmentally friendly, as zinc is a naturally occurring element and is relatively non-toxic to humans and aquatic organisms. Overall, zinc ionization for water treatment operates based on the principles of antimicrobial action, corrosion control, and scale inhibition, providing an effective and environmentally friendly solution for improving water quality and safety in various applications.
Zinc Ion Generation
Zinc ionization systems typically involve the introduction of zinc ions into the water supply. This can be achieved through using electrodes made of zinc alloys to release zinc ions into the water through electrolysis.
Corrosion Control
Zinc ions can also help to mitigate corrosion in water distribution systems by forming a protective layer on metal surfaces. This layer acts as a barrier, preventing the corrosion of pipes, fittings, and other metallic components in the plumbing system. This can help to extend the lifespan of infrastructure and reduce the risk of leaks and pipe failures.
Scale Inhibition
Zinc ionization can also help to prevent the formation of scale deposits in water systems. By interfering with the crystallization process of minerals such as calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate, zinc ions can inhibit the buildup of scale on surfaces such as pipes, fixtures, and appliances.
Antimicrobial Properties
Zinc ions have antimicrobial properties, which can inhibit the growth and proliferation of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms in water. When introduced into the water supply, zinc ions can disrupt the cellular membranes of microorganisms, interfere with their metabolic processes, and ultimately lead to their inactivation or death.